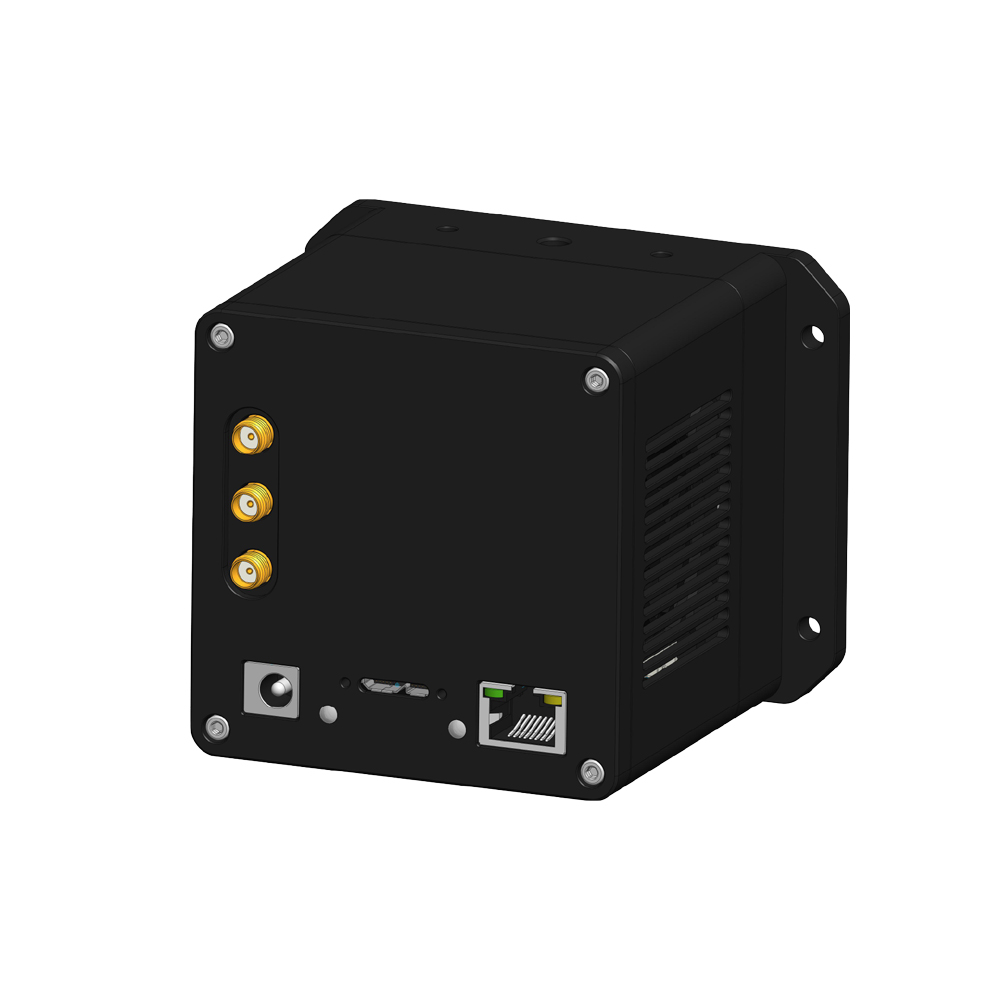
sCCD Series
Product Introduction
The sCCD series is designed for high-sensitivity and low-noise spectroscopy and low-light imaging applications. It utilizes Teledyne e2v high-performance CCD devices (such as CCD261), offering high quantum efficiency and low readout noise across the 250–1050 nm spectral range. This makes it ideal for Raman spectroscopy, photoluminescence/fluorescence, hyperspectral imaging, and other weak signal detection scenarios. Typical configurations feature 15 µm pixel size with 2048 × 264 resolution line/area array combinations, balancing photon collection capability with spectral resolution.
The camera is equipped with TEC cooling and closed-loop temperature control, capable of reducing sensor operating temperature by approximately 40 °C below ambient. It incorporates an anti-condensation optical structure to ensure stability and dark current suppression under low-temperature and long-exposure conditions. The camera supports 8/16-bit data output with built-in buffer memory, offering USB 3.0 and GigE high-speed interfaces (model dependent) to meet continuous high-speed acquisition and long-term experimental link reliability requirements.
It supports free-running, software/hardware triggering, and external device timing synchronization. Bundled with ToupView/CLView and cross-platform SDK (Windows/Linux; C/C++/C#/Python/MATLAB) for easy system integration and custom development.
Product Features
- Teledyne e2v high-sensitivity CCD (e.g., CCD261), optimized for low-light/spectroscopy applications
- Spectral response 250–1050 nm, quantum efficiency up to 95% @ 800 nm (device dependent)
- Resolution 2048 × 264, 15 µm pixel size; effective sensor area approx. 30.72 mm × 3.96 mm
- Low readout noise: typical 3 e⁻ rms (model/readout mode dependent)
- Shutter type: Global exposure (CCD), suitable for Raman/hyperspectral synchronous acquisition
- TEC cooling with closed-loop temperature control, typical ΔT ≈ 40 °C (below ambient), significantly reducing dark current
- Anti-condensation optical structure, suppressing condensation under low-temperature and long-exposure conditions
- Data interface: USB 3.0 / GigE
- Data bit depth: 8-bit / 16-bit
- Built-in 512 MB buffer (4 Gb DDR3), ensuring stable transmission
- Operating temperature: −30 to +45 °C; Storage: −40 to +60 °C; Humidity: 0–95% RH (non-condensing)
- Lens mount: TBD (subject to final model specifications)
- Power supply: 12 V adapter; optimized for long-term stable operation (model dependent)
- Environmental adaptability: −30 to 60 °C, 20–80% RH (non-condensing, model dependent)
- Bundled with ToupView/CLView; Windows/Linux SDK provided (C/C++/C#/Python/MATLAB)
- Supports on-site firmware upgrades; compliant with CE / FCC / RoHS (model dependent)
Product Models
Teledyne e2v sCCD (Area Array) | QE up to 95% @ 800 nm, 300–1000 nm, TEC Cooling (ΔT ≈ 40 °C), USB3/GigE, for Raman/Fluorescence/Hyperspectral Imaging
| Model | Sensor / Size | Resolution | Pixel Size | Shutter | Frame Rate | Interface | Dynamic Range |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sCCD01AM |
Teledyne e2v CCD261 (sCCD)
1.8" (30.97 mm) | 30.72 mm × 3.96 mm
|
0.54 MP (2048×264) | 15 µm × 15 µm | Global Shutter |
TBD @ 2048×264
|
USB 3.0 / GigE |
-
|
View Details |
Package Contents #
Standard kit and packing information for the sCCD01AM Series thermoelectrically cooled sCCD scientific cameras.
Standard Items in the Case
- Camera body (thermoelectrically cooled sCCD scientific camera)
- Power adapter (input: AC 100–240 V 50 Hz/60 Hz, output: DC 19 V 4 A)
- I/O cable (7-pin cable or extension cable)
- USB 3.0 and GigE cables
- Lens (optional)
Product Dimensions #
Mechanical dimensions reference for the sCCD01AM Series thermoelectrically cooled sCCD scientific cameras.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore essential knowledge about scientific-grade CCD cameras.
Advantages: sCCD cameras offer exceptional quantum efficiency, excellent linearity, and extremely low read noise—perfect for spectroscopy, astronomy, and high-precision microscopy.
Limitations: They typically read out more slowly, draw more power, and cost more to manufacture than sCMOS systems.
In-Depth Product Insights
CCD Architecture and Operating Principles
CCD sensors comprise arrays of capacitors that shift accumulated charge line by line after each exposure, converting the charges into voltage outputs. This analog process yields ultra-low noise and excellent uniformity.
Outstanding Sensitivity and Stability
Large full-well capacity and minimal readout circuitry deliver exceptional signal-to-noise ratio and quantum efficiency (QE), enabling the detection of faint signals such as fluorescence, spectral emissions, and astronomical objects.
Readout Speed and Architecture Choices
Scientific CCDs typically offer adjustable readout rates from 0.1 to 20 MHz to meet diverse workflow demands. Full-frame designs deliver the highest QE, frame-transfer sensors enable rapid buffering, and interline architectures mitigate smearing.
Deep Cooling and Dark Current Control
sCCD systems often integrate thermoelectric (TE) or liquid-nitrogen cooling to suppress dark current, boost SNR, and ensure stability for long exposures or low-light conditions.
High Dynamic Range and Linearity
CCD technology supports highly linear, wide-dynamic-range imaging—ideal for grayscale quantification, spectral analysis, and any workflow that demands precise high dynamic range performance.
Key Application Areas
How scientific-grade CCD cameras empower advanced research and industry.
Astronomical Imaging
Ultra-low noise and high quantum efficiency make sCCDs ideal for deep-sky observation, planetary imaging, and spectral surveys, supporting long exposures that capture faint starlight.
Fluorescence & Spectral Microscopy
High sensitivity and linear response suit FRET, Raman spectroscopy, fluorescence lifetime imaging, and other quantitative microscopy techniques.
High Dynamic Range Imaging
Wide dynamic range and high bit depth capture bright and dark detail simultaneously—ideal for materials inspection, quality control, and HDR imaging.
X-ray & Neutron Imaging
Pairing high quantum efficiency with scintillators enables high-quality X-ray and neutron imaging for non-destructive testing and materials science.
Cold Atom & Quantum Imaging
Extremely low noise and high sensitivity—combined with deep cooling—detect single-photon events for BEC, ion-trap, and quantum-dot experiments.
Spectral Analysis
Exceptional linearity and stability, combined with spectrometers, enable precise measurements for chemical analysis, environmental monitoring, and more.
sCCD Technology Highlights
- Ultra-low read noise
- High quantum efficiency (QE > 95%)
- Excellent linear response
- Robust long-exposure performance
- High dynamic range imaging
- Deep cooling capability
- Single-photon detection
- Consistently stable image quality