Product Models
| Model | Sensor / Size | Resolution | Pixel Size | Shutter | Frame Rate | Interface | Dynamic Range |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
No product data available |
||||||||
Frequently Asked Questions
Learn more about SWIR short-wave infrared camera technology
Deep Understanding of SWIR Cameras
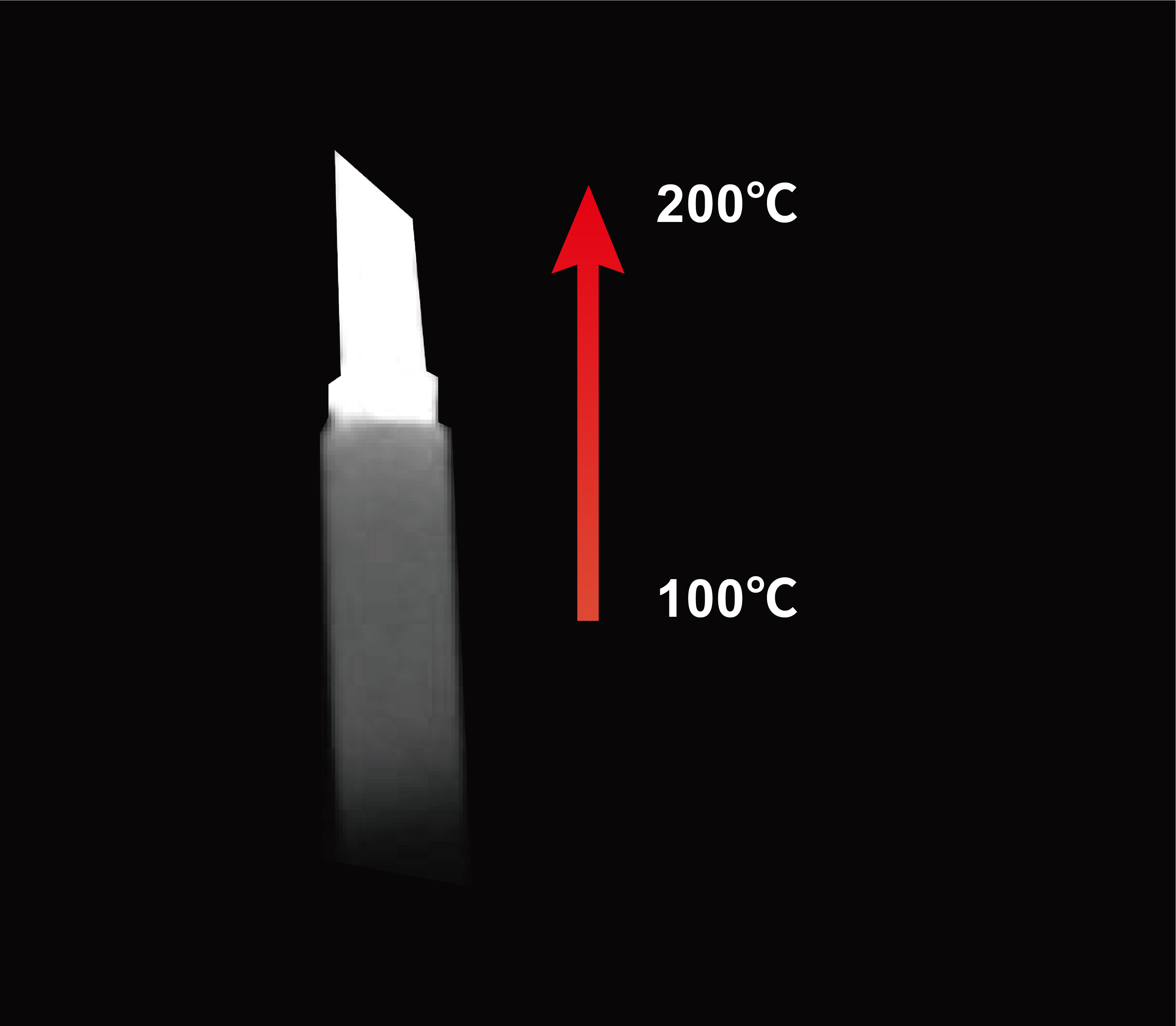
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) cameras and their core sensors are important components of advanced imaging systems. SWIR technology covers the 900–1700 nanometer wavelength band and has excellent penetration capabilities in harsh environments, such as penetrating fog, smoke, and dust to achieve clear imaging under extreme conditions.
SWIR cameras primarily rely on short-wave infrared light reflection, similar to the visible light band, complementing the application range that thermal imaging cameras (LWIR) cannot cover, providing more complete imaging solutions. They are compact and flexibly integrated, making them easy to apply in various industrial and commercial systems.
The high resolution and high sensitivity of SWIR cameras can meet precision detection and high-requirement applications, capable of detecting minute changes and anomalies in samples, making them very suitable for quality control and defect detection. Some models support cooling, further ensuring imaging quality in high-temperature or high-noise environments.
To reduce system costs and improve integration efficiency, modern SWIR cameras commonly adopt standard optical interfaces and compact designs to accommodate broader application requirements. With the continuous development of imaging markets and technology, SWIR cameras have become one of the key technologies for high-end imaging and sensing in multiple industries due to their unique advantages.
Application Examples
Demonstration of SWIR camera applications in real-world scenarios
More Application Industry References
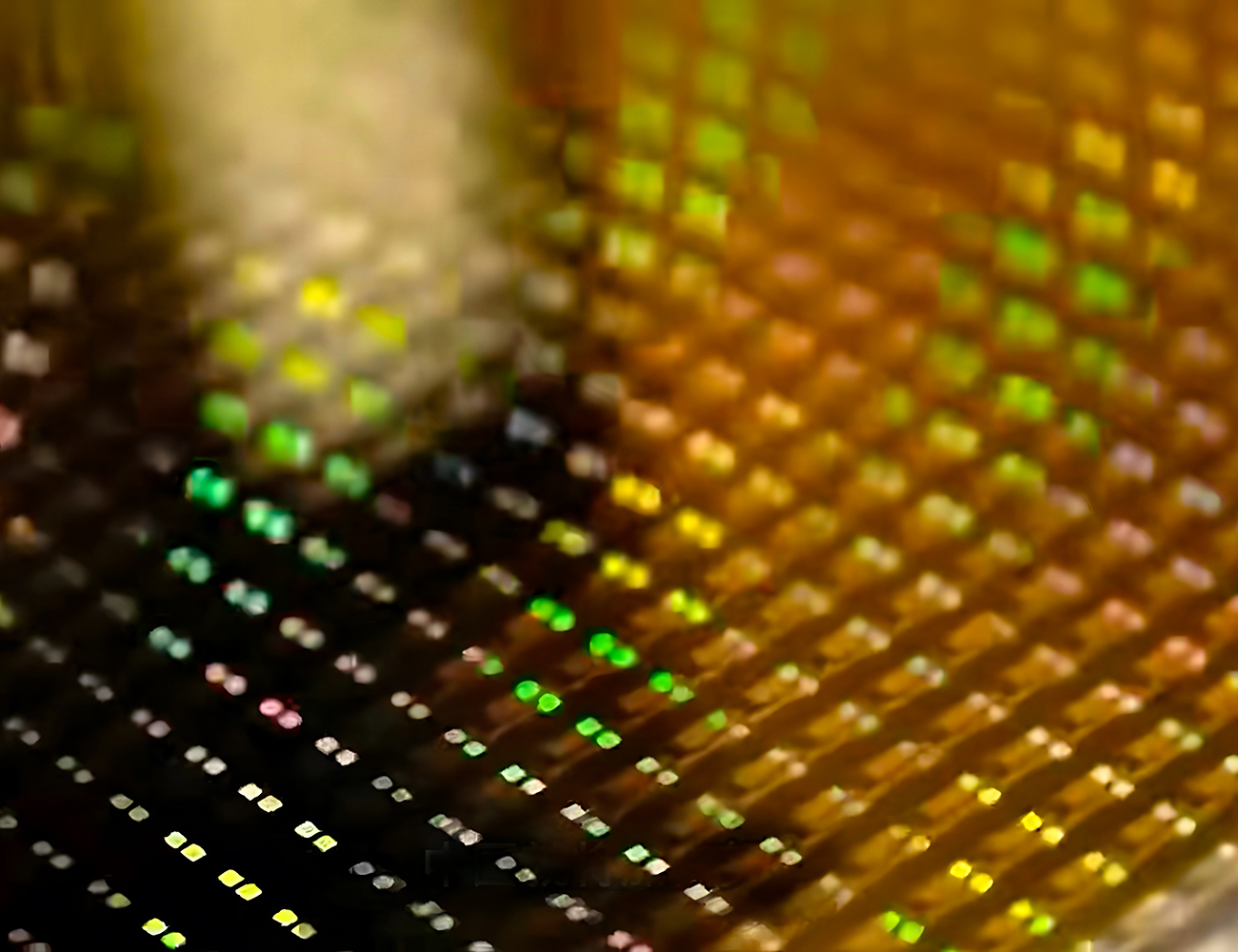
- Semiconductor Industry: Solar cell and chip inspection
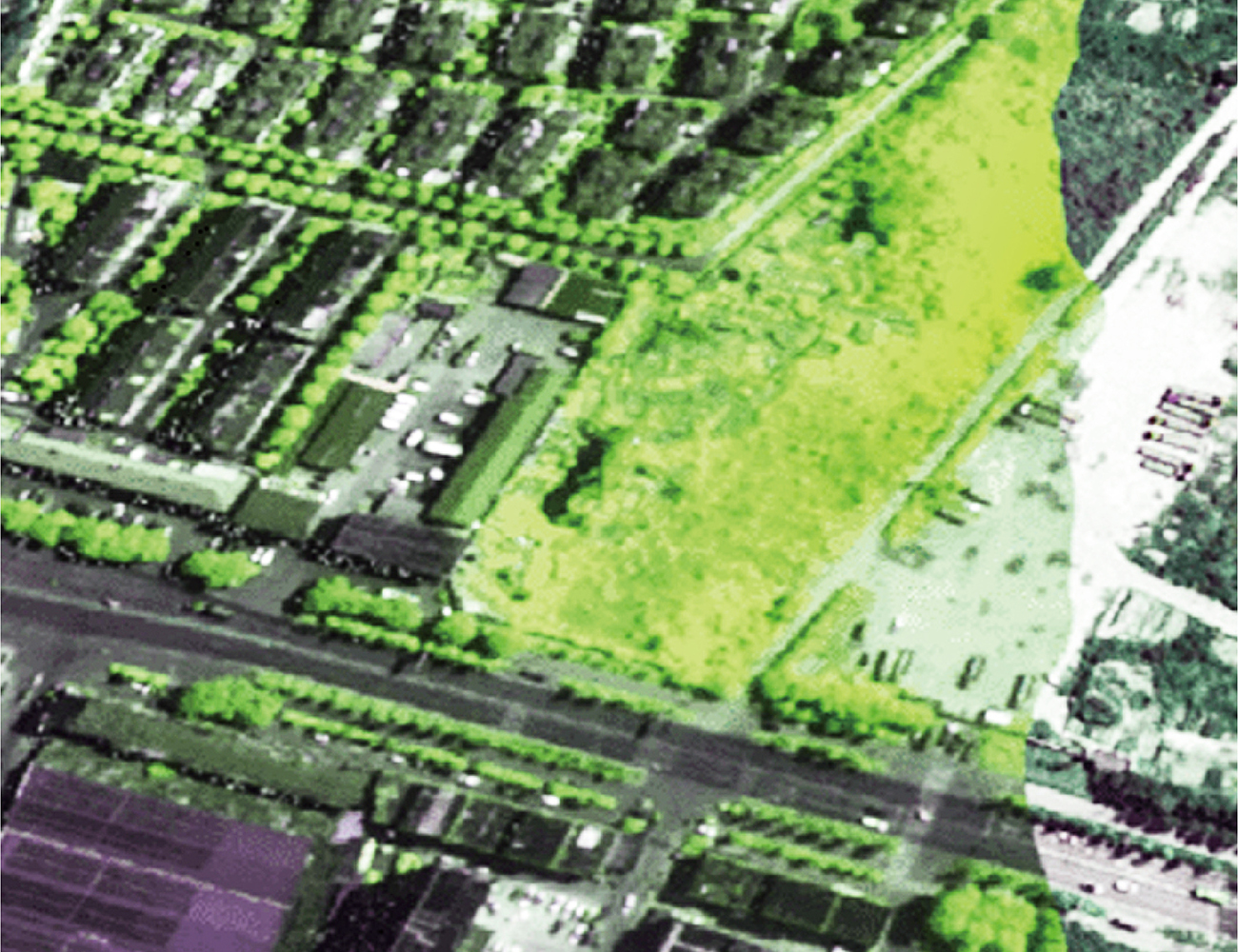
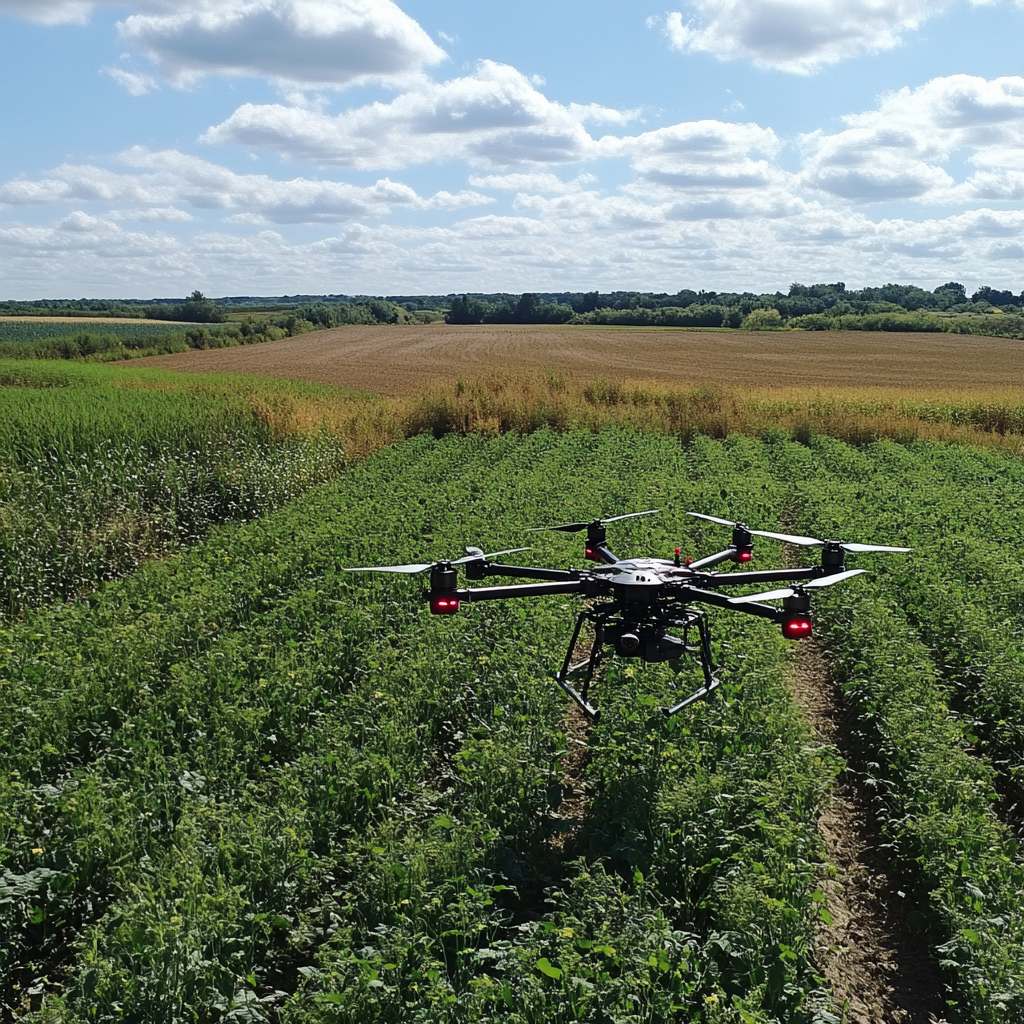
- Agriculture: Spectral remote sensing applications via multirotor aircraft
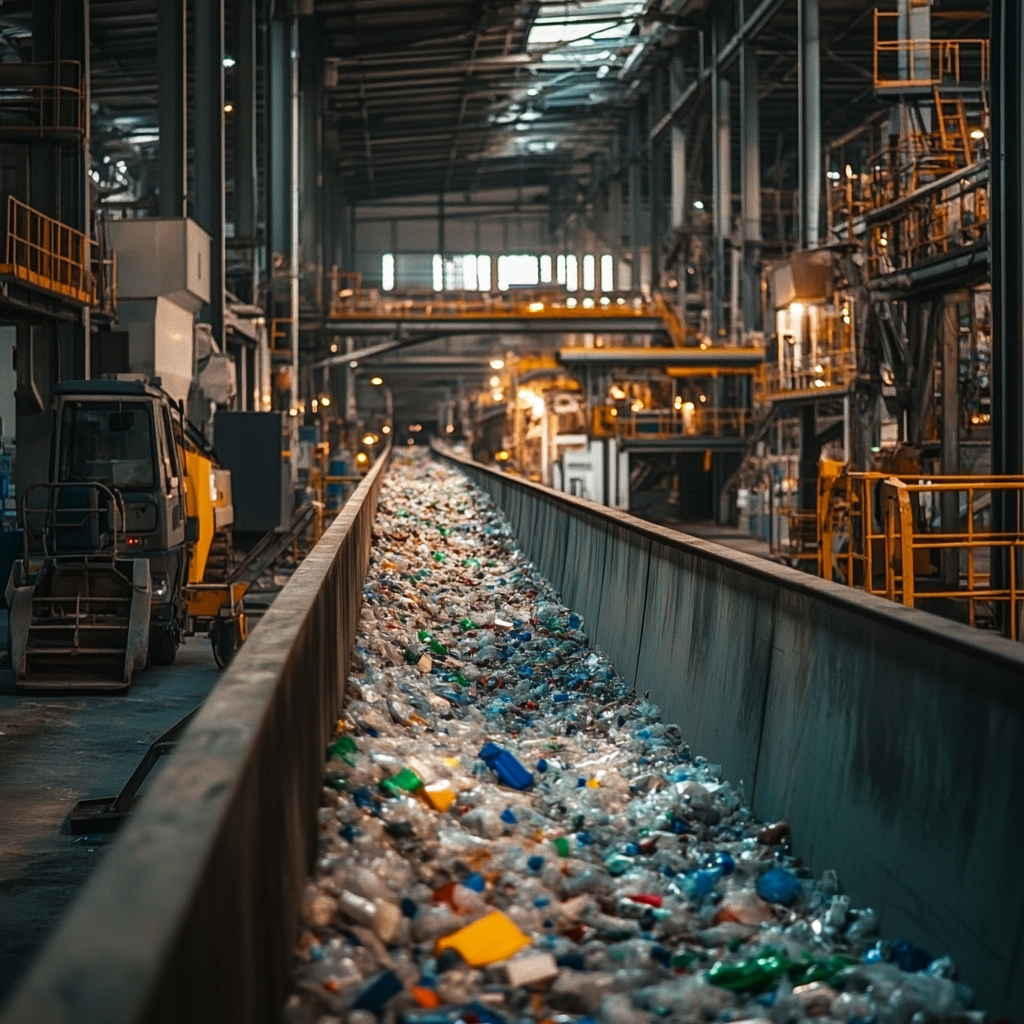
- Recycling Industry: Material sorting of plastics, waste, and other materials
- Medical Imaging and Research: Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging
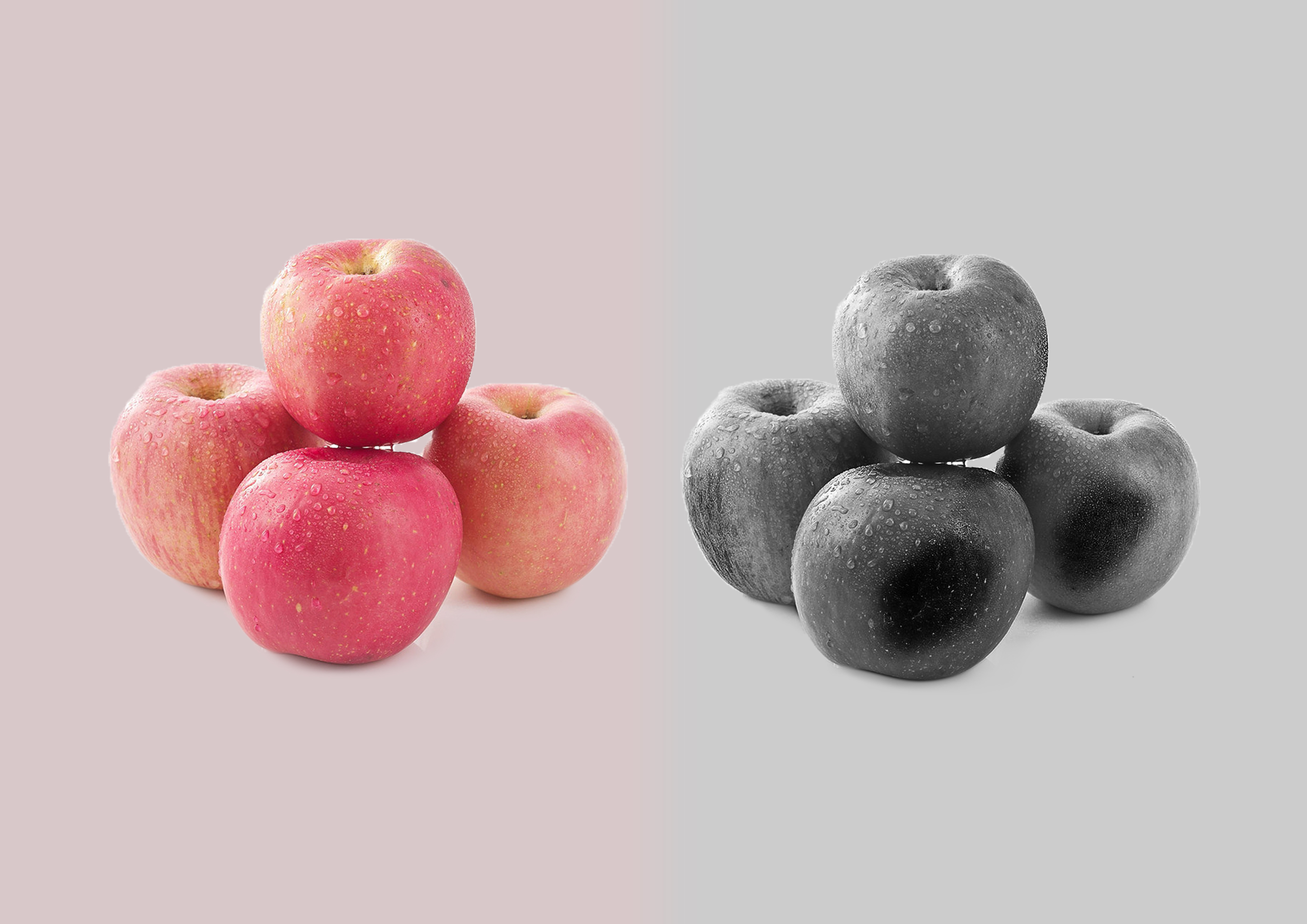
- Food Industry: Quality inspection and grading
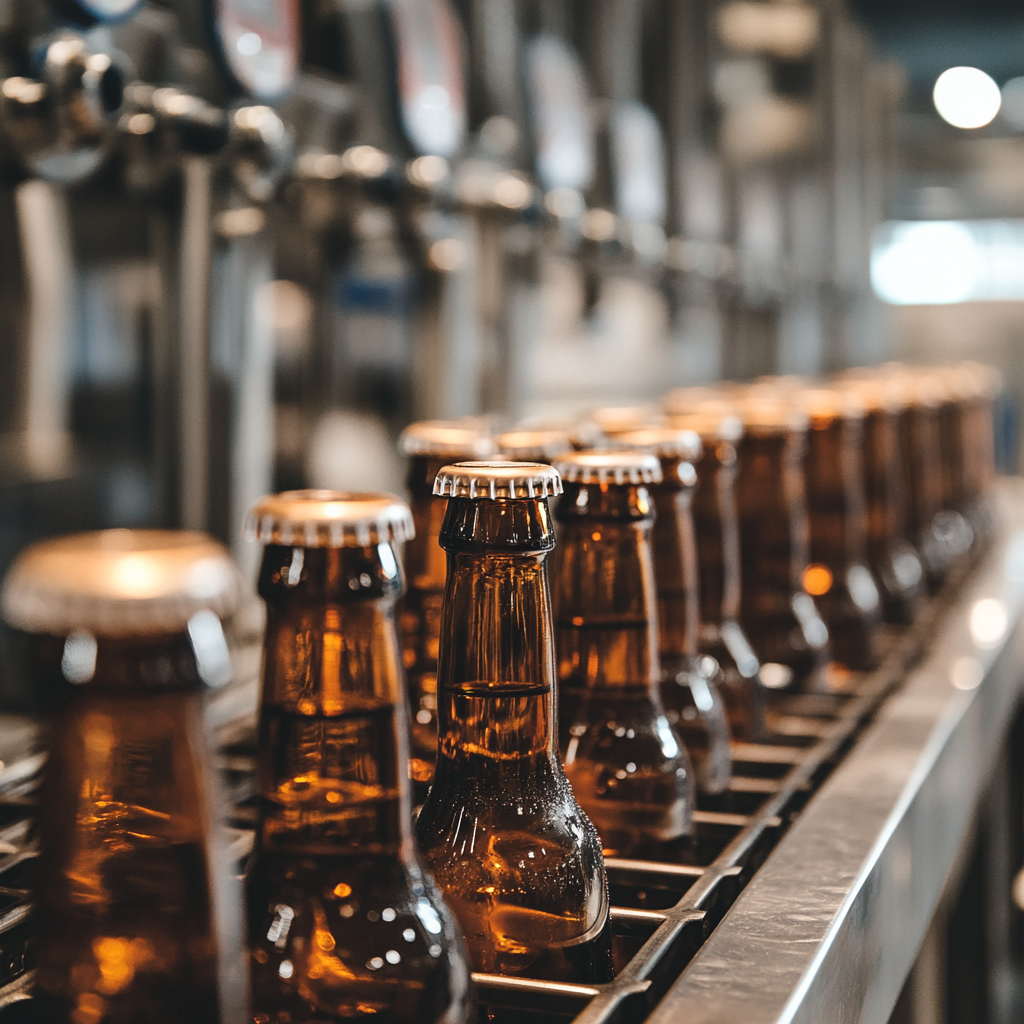
- Beverage Industry: Liquid level detection in opaque containers
- Packaging: Seal inspection
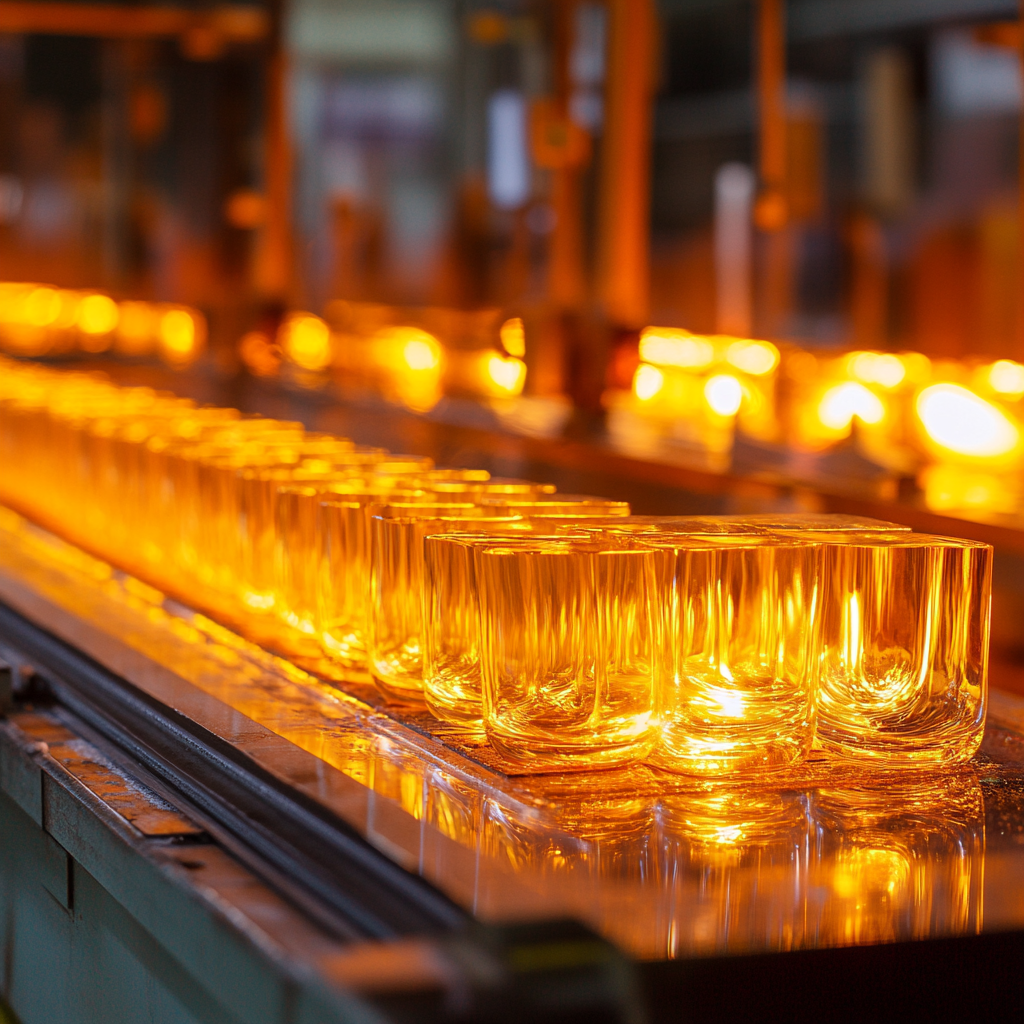
- Glass Industry: High-temperature glass penetration defect detection
- Printing Industry: See-through hidden features
- Video Surveillance: Visual enhancement (e.g., smoke penetration)
- Security: Counterfeit detection, such as currency, wigs, or skin